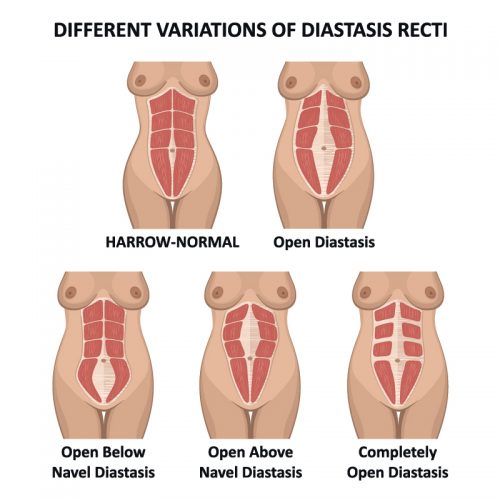
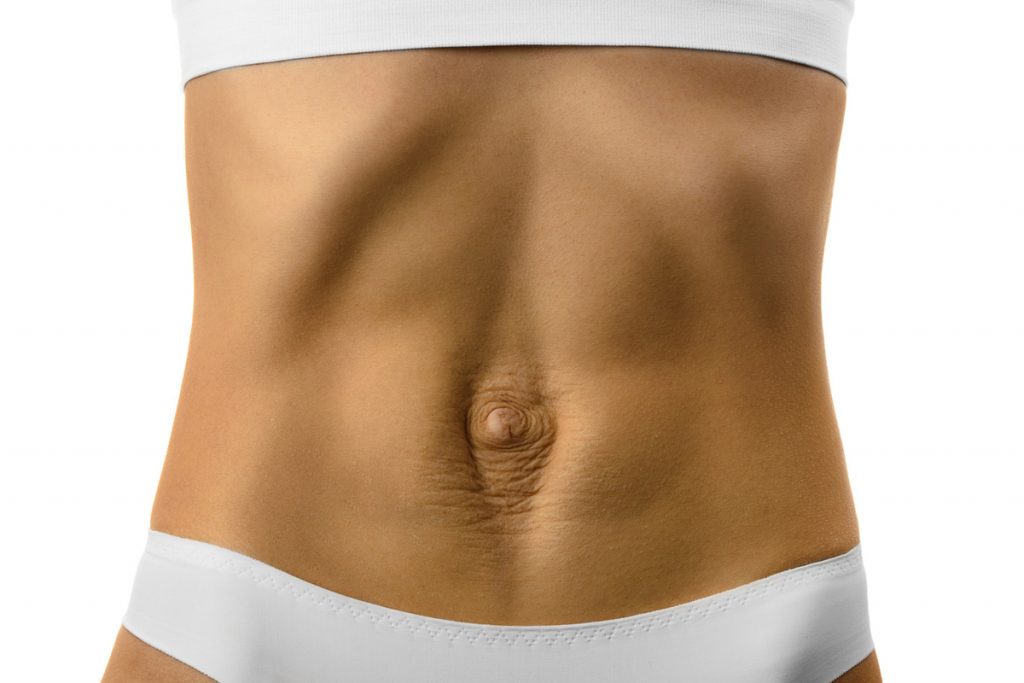
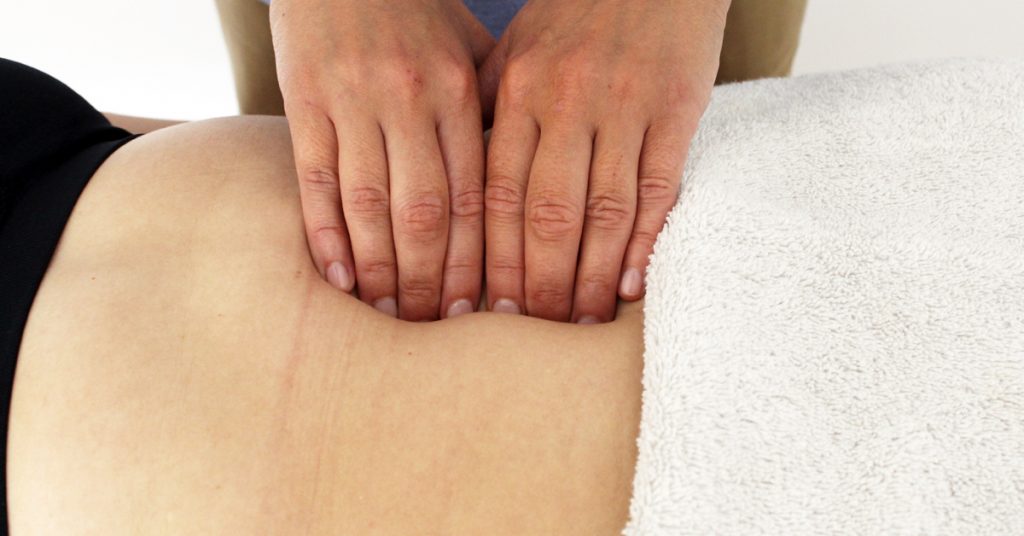
Diastis Recti is when the rectus muscles of the abdomen separate as a result of damage to the connective tissue that, under normal conditions, holds them together.
Diastasis is more common than people realise and people are often concerned more with how they look rather than the functional aspect of the problem, which should be more of a concern. A straight separation can happen to anyone, regardless of age, sex, or whether you do sports regularly or not.